As the “Musk Empire” pivots toward an AI-first future, the battle for computing power is literally leaving the planet. With Elon Musk now having the increased voting power at Tesla to push high-risk AI projects and the massive launch capacity of SpaceX’s Starship, the concept of “Orbital AI Hubs” has moved from science fiction to a 2026 strategic roadmap.
Below is a detailed comparison of the emerging Space Data Center technology versus traditional Earth-based AI Hubs.
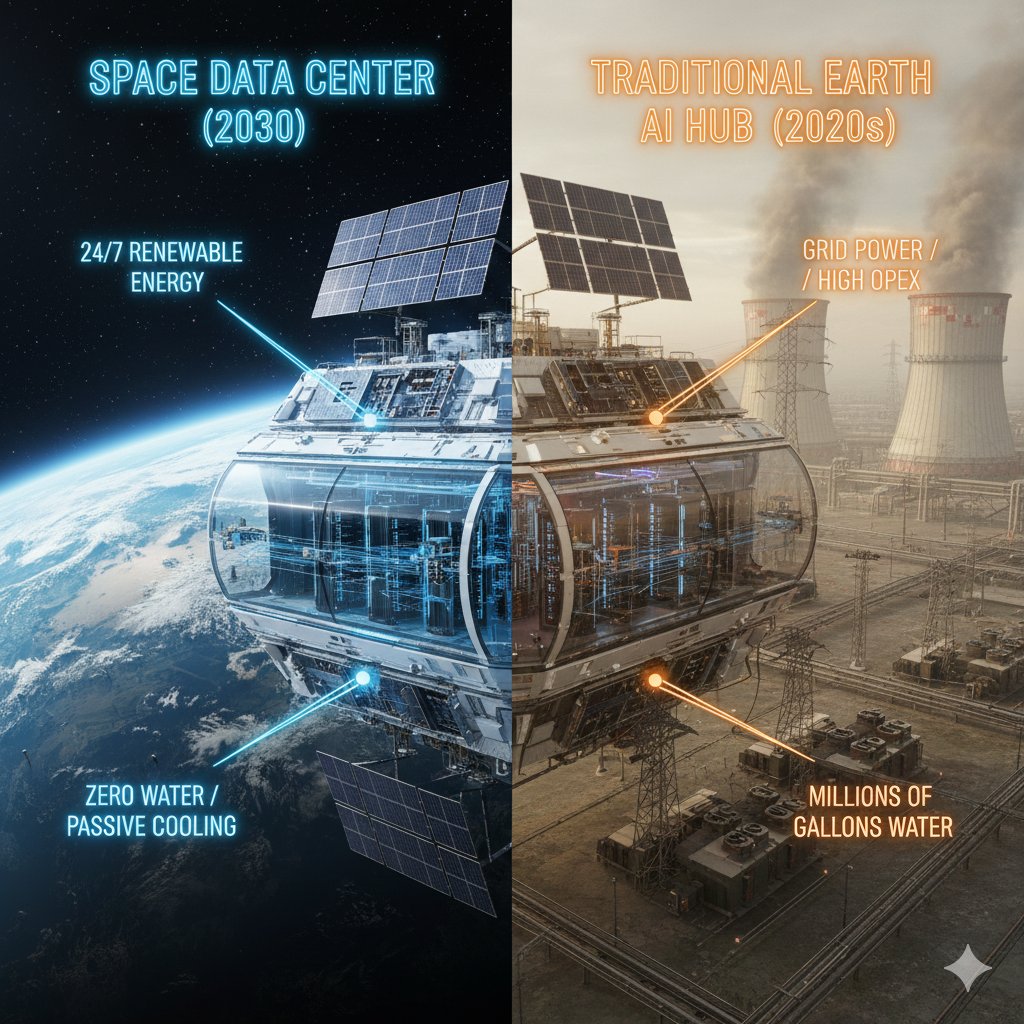
🚀 Space Data Centers vs. 🌍 Earth-based AI Hubs
| Feature | Space Data Centers (Orbital AI) | Earth-based AI Hubs (Hyperscale) |
| Power Source | 24/7 Solar: No night, clouds, or atmosphere. 8-10x more energy per $m^2$. | Grid-Dependent: Vulnerable to blackouts, peak pricing, and weather. |
| Cooling | Passive Radiative: Heat is shed into the -270°C vacuum. Zero water used. | Active Liquid/HVAC: Consumes millions of gallons of water and ~40% of total energy. |
| Expansion | Unlimited: No land permits or NIMBY (Not In My Backyard) opposition. | Highly Constrained: Years-long battles for land, permits, and power grid access. |
| Latency | 5-10ms (LEO): Faster than cross-country fiber for long-distance data. | 1-2ms (Local): Best for real-time edge use, but scales poorly over distance. |
| Main Threat | Radiation & Debris: Requires “space-grade” hardened chips and shielding. | Natural Disasters: Earthquake, flood, and geopolitical instability. |
| Maintenance | Hands-Off: Zero physical repairs possible; requires 100% autonomy. | Technician-Led: Easy part replacement and manual hardware upgrades. |
| Cost Profile | High CAPEX / Low OPEX: Massive launch costs but near-zero monthly utility bills. | Low CAPEX / High OPEX: Cheaper to build, but “renting” power and water is permanent. |
The “Starlink V3” Edge
Elon Musk’s upcoming Starlink V3 satellites are expected to be the first “compute-capable” nodes in this network.1 Unlike previous generations designed only for relaying signals, these will feature:
-
Modular GPU Housings: “Drop-in” units for NVIDIA-grade AI accelerators.2
-
Terabit-Class Interlinks: Laser-based communication 40% faster than terrestrial fiber.3
-
Starship Deployment: The ability to launch 60+ “data satellites” at a time, bringing the cost per kilogram down from $2,700 to roughly $200.4
Why the Trillion-Dollar Race?
Analysts at Morgan Stanley and McKinsey project that space-based computing could capture up to 10% of the global data center market by 2040, representing over $100 billion in annual revenue.5
-
For Tesla: Space centers provide the “infinite” training ground for the Optimus robot and Full Self-Driving AI without taxing local power grids.6
-
For SpaceX: It transforms the company from a “transportation” business into a “utility” business, owning the infrastructure that powers the global AI economy.
700 701 702 703 704 705 706 707 708 709 710 711 712 713 714 715 716 717 718 719 720 721 722 723 724 725 726 727 728 729 730 731 732 733 734 735 736 737 738 739 740 741 742 743 744 745 746 747 748 749 750 751 752 753 754 755 756 757 758 759 760 761 762 763 764 765 766 767 768 769 770 771 772 773 774 775 776 777 778 779 780 781 782 783 784 785 786 787 788 789 790 791 792 793 794 795 796 797 798 799 800 801 802 803 804 805 806 807 808 809 810 811 812 813 814 815 816 817 818 819 820 821 822